Peanut butter has become one of the most beloved spreads around the globe — creamy, flavorful, and packed with nutrients. Behind every smooth spoonful lies a crucial choice: the type of peanut used, peanut butter production, selecting the right variety determines not only the flavor but also the texture, color, and shelf stability of the final product.
For entrepreneurs, food processors, and investors looking to establish or optimize a peanut butter production line, understanding which peanuts perform best is essential. The difference between a good product and an excellent one often begins at the very first step — choosing the right peanut. we’ll explore the major peanut types, their characteristics, and how they impact the production process and final product quality.

1. Overview of Peanut Varieties
Globally, peanuts are divided into four major commercial types:
- Runner peanuts
- Virginia peanuts
- Spanish peanuts
- Valencia peanuts
Each variety has unique characteristics affecting oil content, flavor, and texture. Knowing their differences helps manufacturers produce peanut butter that matches consumer expectations in different markets.
1.1 Runner Peanuts – The Industry Favorite
Runner peanuts are the most common choice for large-scale peanut butter production. They are primarily grown in Georgia, Alabama, Florida, and Texas, and are valued for their uniform kernel size and consistent roasting performance.
Main characteristics:
- Kernel size: Medium and uniform
- Oil content: Around 46–48%
- Flavor: Balanced and mild
- Best for: Smooth, commercial peanut butter
Because of their uniformity, Runner peanuts roast evenly, which ensures a consistent flavor and color. The balanced oil content produces a creamy, spreadable texture that fits consumer preferences for standard peanut butter. Most major global peanut butter brands rely heavily on this variety due to its reliability and availability.
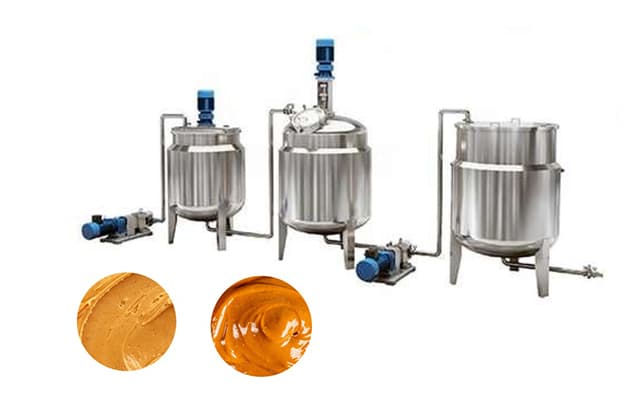

1.2 Virginia Peanuts – Premium Texture and Flavor
Virginia peanuts are recognized for their large kernel size and robust flavor. They are primarily grown in Virginia and the Carolinas, and are often marketed as gourmet peanuts.
Key characteristics:
- Kernel size: Large
- Oil content: 45–47%
- Flavor: Rich, slightly sweet
- Best for: Chunky or premium peanut butter varieties
Because of their larger kernels, Virginia peanuts are often used in chunky-style peanut butter where pieces of nuts add to the texture. Their bolder flavor makes them ideal for premium brands seeking a stronger, nutty taste.
1.3 Spanish Peanuts – High Oil and Bold Aroma
Spanish peanuts are smaller, rounder, and have a reddish-brown skin. They contain more oil than other varieties, giving them a strong flavor and natural creaminess.
Key characteristics:
- Kernel size: Small
- Oil content: 48–50%
- Flavor: Intense and aromatic
- Best for: Natural or artisan peanut butter
Because of their high oil content, Spanish peanuts produce peanut butter with a richer taste and smoother consistency. They are particularly favored by smaller producers or artisanal brands that emphasize natural ingredients and authentic flavor without adding stabilizers.

1.4 Valencia Peanuts – Naturally Sweet and Organic-Friendly
Valencia peanuts are known for their sweet flavor and are popular in natural and organic peanut butter products. Typically, each shell contains three or more small kernels, and they are mainly cultivated in New Mexico.
Key characteristics:
- Kernel size: Small, three per pod
- Oil content: 49–50%
- Flavor: Sweet and mild
- Best for: Organic and family-friendly peanut butter
Their natural sweetness makes Valencia peanuts a preferred choice for all-natural peanut butter aimed at health-conscious consumers or children. They are often grown under pesticide-free conditions, which strengthens their appeal in the organic market segment.
2. Matching Peanut Varieties to Market Needs
Selecting the right peanut type depends on your target market, product positioning, and production capacity. Below is a simple guide:
| Market Type | Ideal Peanut Variety | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Mass-market peanut butter | Runner | Consistent, smooth, affordable |
| Premium brands | Virginia | Rich flavor, ideal for chunky type |
| Natural & organic markets | Valencia or Spanish | High oil, natural sweetness |
| Export-oriented products | Runner or Virginia | Reliable quality and texture |
| Artisan & small-scale brands | Spanish | Distinct flavor, handcrafted appeal |
Understanding the connection between peanut type and market demand helps manufacturers design products that stand out and meet local tastes effectively.

3. Peanut Properties and Their Impact on Peanut Butter Quality
The choice of peanut influences the texture, color, oil separation, and overall sensory experience of the final peanut butter.
3.1 Oil Content and Consistency
Peanuts with higher oil content, like Spanish and Valencia, produce a naturally creamy product but may require additional stabilization to prevent oil separation during storage.
Meanwhile, Runner peanuts strike a balance between creaminess and stability, making them ideal for commercial production lines that aim for long shelf life.
3.2 Flavor Profile
- Runner peanuts: Mild, adaptable for blending
- Spanish peanuts: Bold, roasted aroma
- Virginia peanuts: Rich, gourmet flavor
- Valencia peanuts: Naturally sweet
Roasting enhances these flavors, so choosing a peanut variety that complements your roasting method is crucial.
3.3 Roasting Performance
Uniform kernel size ensures even roasting — a key factor in flavor consistency. Runner peanuts excel in this area, while Virginia and Spanish varieties may need stricter temperature control.
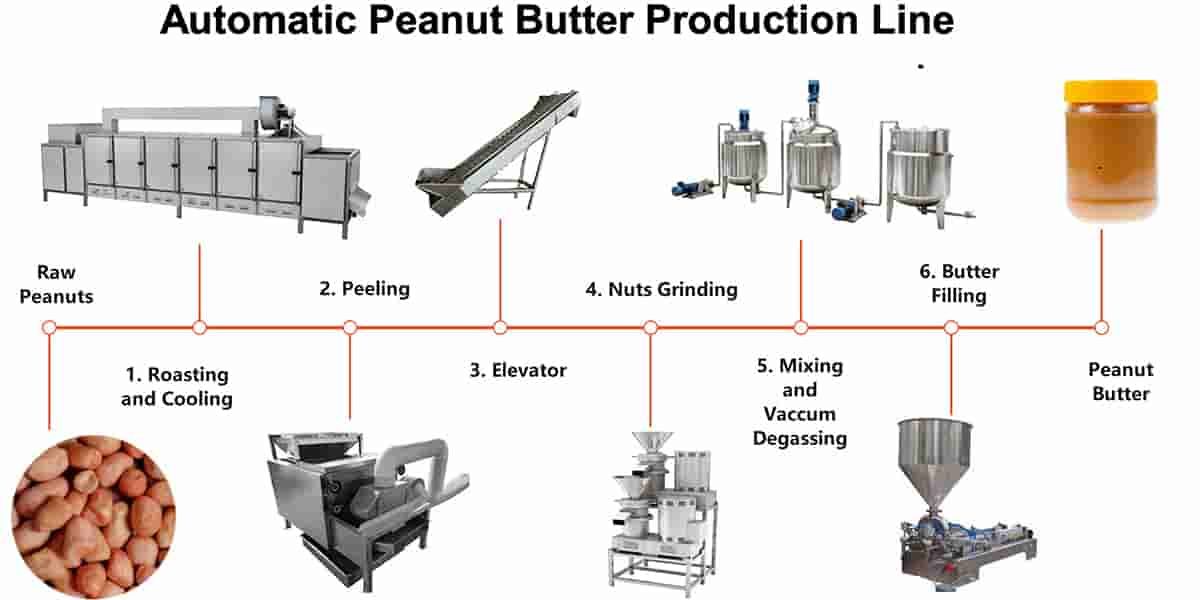
4. The Peanut Butter Production Process
To produce high-quality peanut butter, every processing step must be optimized to match the peanut type. The main stages include:
4.1 Cleaning and Sorting
Raw peanuts are cleaned to remove impurities, stones, and dust. Sorting ensures uniform size for even roasting.
4.2 Roasting
Roasting typically occurs between 160°C and 180°C depending on peanut size and desired flavor. Proper roasting develops flavor while preventing over-browning.
4.3 Cooling and Skin Removal
Roasted peanuts are rapidly cooled to stop the cooking process. Then, the skins are removed using air friction or mechanical peeling.
4.4 Grinding and Milling
This is the most critical stage, where peanuts are transformed into butter.
High-speed industrial peanut butter grinders use precision-engineered stainless-steel blades to achieve the desired texture — from extra smooth to chunky. The grinding gap can be adjusted for different product styles.
4.5 Mixing and Homogenizing
Ingredients such as salt, sugar, or stabilizers may be added. For natural peanut butter, this step is often skipped to maintain purity.
4.6 Filling and Packaging
The final product is filled into jars or containers using automatic or semi-automatic filling machines designed for high hygiene and efficiency.
At this stage, product consistency and filling temperature play key roles in ensuring a professional appearance and long shelf life.
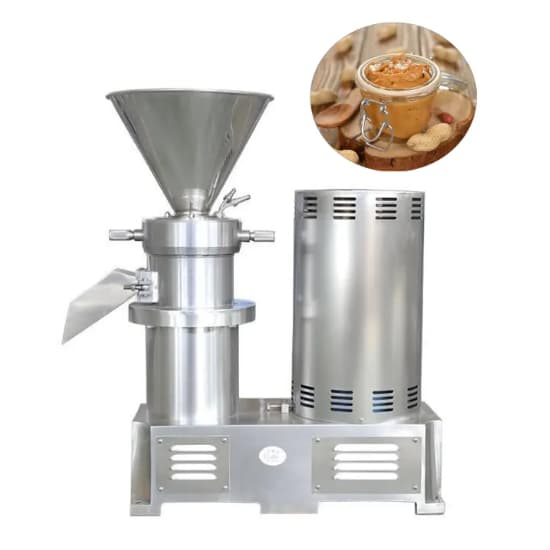

5. Key Technical Factors in Peanut Butter Production
| Parameter | Ideal Value | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture content | 6–8% | Prevents mold and improves roasting quality |
| Roasting temperature | 160–180°C | Controls flavor and oil release |
| Grinding fineness | 100–150 microns | Determines smoothness |
| Oil yield | 45–50% | Depends on peanut type |
| Storage conditions | Cool and dry | Extends shelf life |
A well-designed peanut butter line allows fine-tuning of these parameters to accommodate different peanut types.
For example, modern equipment from DT Food Machine includes adjustable temperature control, variable grinding speeds, and stainless-steel contact parts that ensure hygiene and consistent product quality.
6. Profitability and Market Trends
Peanut butter production continues to grow rapidly worldwide, especially in regions where plant-based proteins and natural foods are trending.
Current trends include:
- Increasing consumer interest in natural and sugar-free peanut butter
- Growing private label and export markets
- Expansion in Asia, Africa, and Latin America
- Rising demand for customized packaging and flavor innovations
Choosing the right peanut type can enhance your profit margins. For instance:
- Runner peanuts are cost-effective and ideal for high-volume sales.
- Spanish peanuts can command premium pricing for their rich flavor.
- Valencia peanuts are popular in organic markets, where consumers are willing to pay more for natural ingredients.
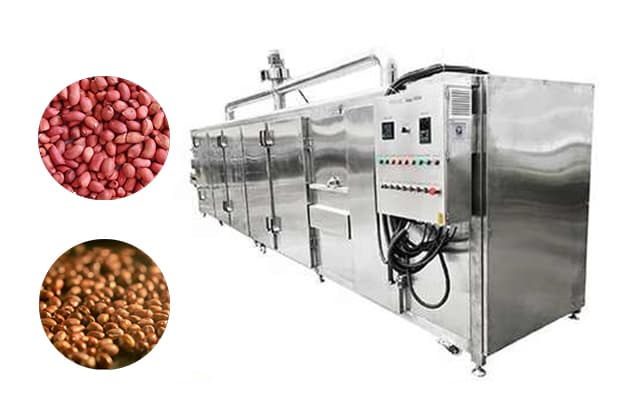

7. Equipment and Production Line Configuration
A standard peanut butter production line typically includes:
- Peanut cleaning and shelling machine
- Roasting system with temperature control
- Cooling and peeling system
- Industrial grinder or colloid mill
- Mixing and homogenizing tanks
- Storage and cooling tanks
- Filling and packaging machine
Each unit plays a vital role in ensuring efficiency, hygiene, and consistent flavor output.
High-performance production systems offered by DT Food Machine are designed to handle different peanut varieties, allowing manufacturers to produce smooth, chunky, or natural peanut butter according to market needs.
8. Selecting Quality Peanuts for Production
When sourcing peanuts, manufacturers should focus on the following:
- Supplier reliability: Consistent quality reduces production downtime.
- Low moisture and aflatoxin levels: Essential for safety and compliance.
- Uniform size: Ensures even roasting.
- Flavor profile testing: Conduct small-scale roasting tests before bulk purchase.
- Storage conditions: Peanuts should be stored in a cool, dry place to maintain freshness.
Building long-term partnerships with peanut suppliers ensures raw material stability and predictable costs, which are vital for industrial-scale operations.
9. Peanut Butter Types and Product Innovation
Manufacturers often diversify their product lines to capture different consumer segments. Common variants include:
| Type | Description | Typical Peanut Variety |
|---|---|---|
| Smooth Peanut Butter | Finely ground, creamy texture | Runner |
| Chunky Peanut Butter | Includes peanut pieces | Virginia |
| Natural Peanut Butter | No additives or stabilizers | Valencia or Spanish |
| Honey Roasted Peanut Butter | Slightly sweetened | Virginia |
| Organic Peanut Butter | Made with pesticide-free peanuts | Valencia |
Adapting product recipes based on peanut characteristics helps differentiate brands and build market loyalty.
10. Quality Control in Peanut Butter Production
Quality control is critical at each stage:
- Raw peanuts: Test for aflatoxin and moisture.
- Roasting: Monitor color and aroma development.
- Grinding: Check viscosity and texture consistency.
- Packaging: Inspect seal integrity and labeling accuracy.
Maintaining these standards ensures consumer safety and brand reputation.
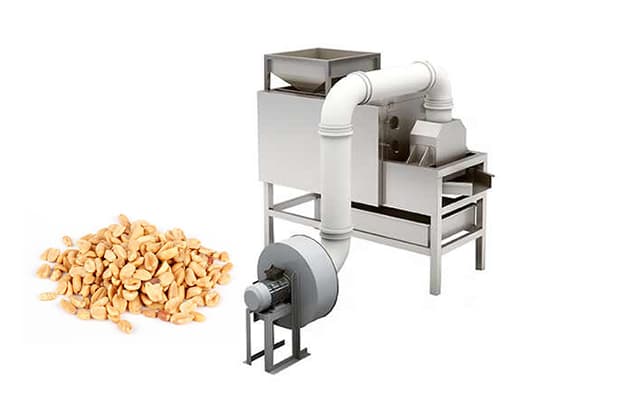

11. Packaging and Shelf Life
Peanut butter should be packaged in airtight containers to prevent oxidation and oil separation. PET jars, glass bottles, or flexible pouches are common.
Adding stabilizers like hydrogenated oil can extend shelf life, but natural brands may rely on vacuum sealing and refrigeration instead. Optimal shelf life ranges from 6 to 12 months, depending on formulation and packaging type.
12. Final Thought
The secret to exceptional peanut butter lies in choosing the right peanut variety and optimizing every production stage.
- Runner peanuts are perfect for mainstream, smooth peanut butter.
- Virginia peanuts deliver texture and bold flavor for premium products.
- Spanish peanuts offer high oil and robust taste for natural butters.
- Valencia peanuts bring natural sweetness ideal for organic markets.
By integrating high-quality equipment and processing systems from DT Food Machine, manufacturers can ensure consistency, efficiency, and superior peanut butter quality across all varieties.
Whether you’re starting a small workshop or building a large-scale production line, understanding peanut characteristics and choosing the right technology will help you create peanut butter that satisfies both consumers and your business goals.
