Starting a peanut butter production business is one of the most promising opportunities in the food processing industry today. Global demand for peanut butter is rising, driven by its health benefits, protein content, and versatility in cooking and snacking. Fakat, many entrepreneurs and small investors wonder: how can you start peanut butter production with a low budget?
We will walk you through every essential step—from understanding the market, sourcing raw materials, and selecting the right equipment, to managing costs and ensuring profitability. Whether you’re planning a small local operation or dreaming of scaling up later, this article will help you build a profitable foundation with minimal investment.
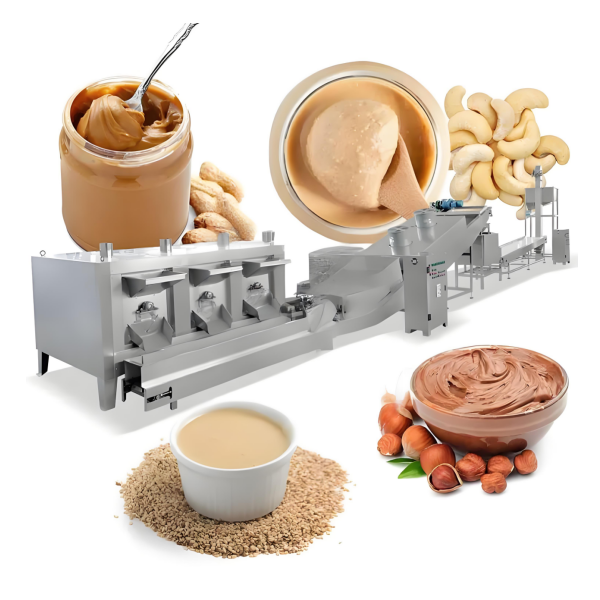

1. Understanding the Peanut Butter Market
Before investing in any equipment or raw materials, it’s vital to analyze the peanut butter market and its trends.
1.1 Dünya Çapında Artan Talep
Peanut butter is consumed across continents—from North America to Africa, Asya, ve Avrupa. It’s no longer limited to sandwiches; consumers now use it in smoothies, protein bars, soslar, and even baked goods. This versatility has created stable year-round demand.
1.2 Profit Margins and Consumer Preferences
Profit margins can range between 30% Ve 60%, depending on scale and distribution strategy. Consumers increasingly prefer natural or organic peanut butter, with fewer additives and sugars. This opens opportunities for small producers to offer artisanal or healthier versions.
1.3 Target Market Options
Small producers can target:
- Local grocery stores or supermarkets
- Health food stores
- Online marketplaces (Amazon, Shopee, Lazada, vesaire.)
- Cafés and restaurants seeking bulk supply
Understanding your audience will shape everything—from packaging design to pricing strategy.
2. Estimating Startup Costs
Starting peanut butter production on a low budget doesn’t mean compromising quality—it means planning smartly. Here’s a breakdown of typical expenses for a small-scale peanut butter production unit.
| Öğe | Tahmini maliyet (Amerikan Doları) |
|---|---|
| Small peanut butter making machine | $1,000 - $3,500 |
| Roasting and cooling equipment | $800 - $2,000 |
| Mixing and filling unit | $1,000 - $2,500 |
| Ambalaj malzemeleri | $300 - $800 |
| Fıstık (raw material) | $400 - $1,000 per ton |
| Miscellaneous (labels, rent, yardımcı programlar) | $500 - $1,000 |
A complete small-scale setup can often begin with an investment of etrafında $5,000 ile $10,000, depending on your location and production volume.
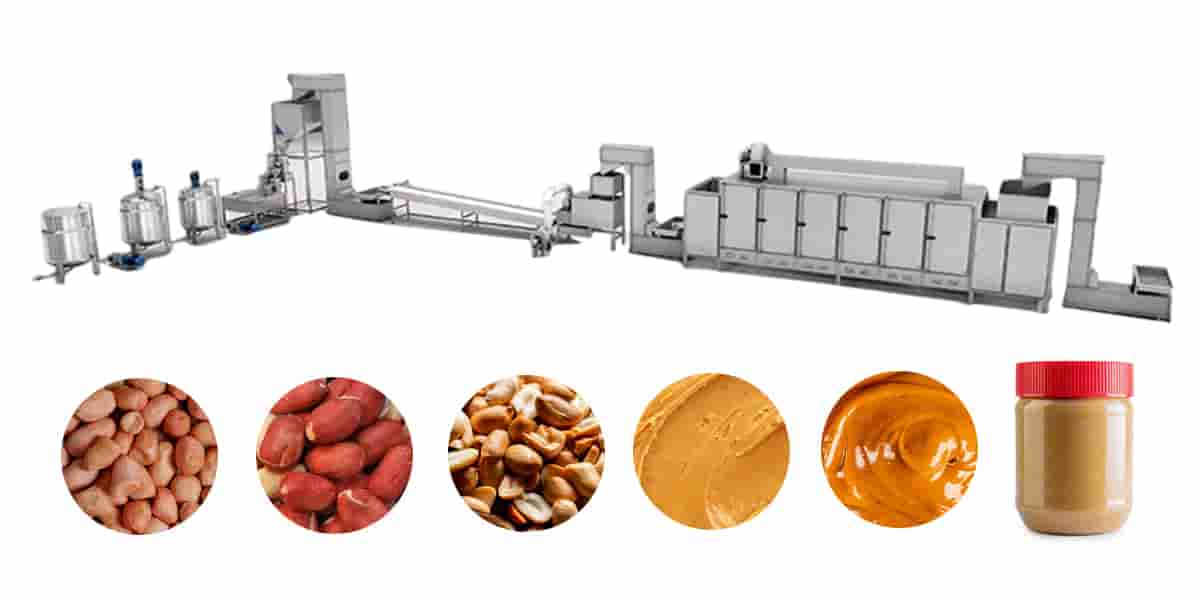

3. Choosing the Right Equipment
Equipment selection is one of the most critical decisions for new entrepreneurs. Reliable and efficient machines can reduce labor costs, üretkenliği artırın, ve tutarlı ürün kalitesi sağlayın.
3.1 Essential Machines You’ll Need
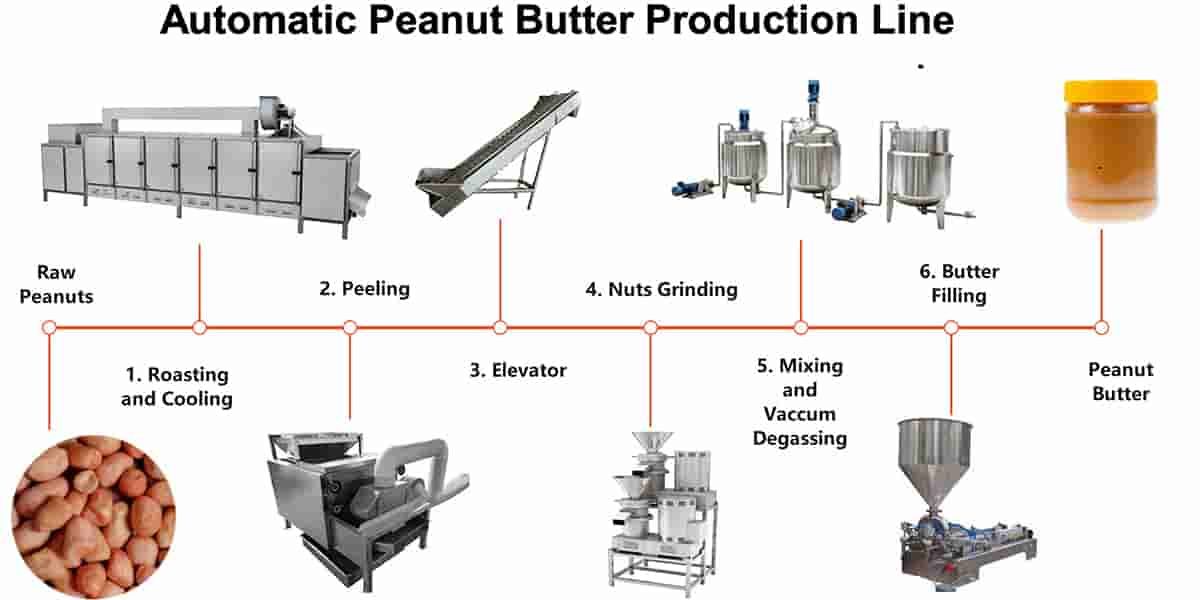
A basic peanut butter production line generally includes:
- Fıstık kavurma makinesi – Ensures even roasting for enhanced flavor.
- Cooling Conveyor or Cooling Tray – Lowers the temperature for grinding.
- Fıstık soyma makinesi – Removes the outer red skin efficiently.
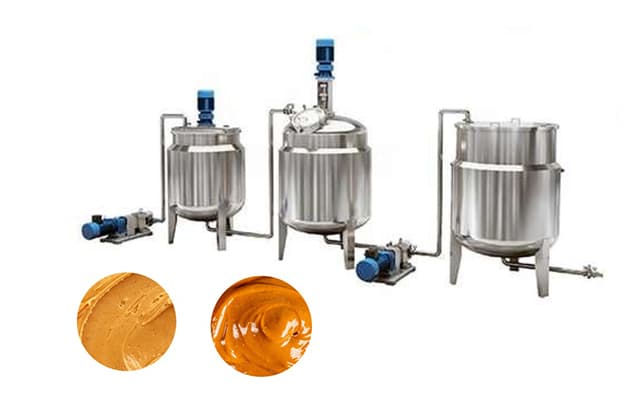
- Fıstık Ezmesi Taşlama Makinesi – Grinds roasted peanuts into a smooth or crunchy paste.
- Mixing and Blending Unit – Mixes peanut paste with salt, şeker, or stabilizers if needed.
- Filling and Sealing Machine – Packs peanut butter into jars or pouches.
3.2 Semi-Automatic vs. Fully Automatic Systems
For low-budget startups, semi-automatic lines are ideal. They require manual input in certain steps but cost significantly less than fully automated ones. As production grows, you can easily upgrade to an automatic system.
3.3 Choosing a Reliable Manufacturer
Partnering with a trusted equipment supplier ensures durability, enerji verimliliği, ve satış sonrası destek.
DT Gıda Makinesi, Örneğin, provides small-scale and modular peanut butter machines suitable for entrepreneurs aiming to start production at lower cost. Their equipment can handle roasting, bileme, Karıştırma, and packaging in one streamlined system—making it easier to begin production with limited capital.
4. Sourcing Raw Materials
Peanuts are the backbone of your product. Quality peanuts directly affect the flavor, doku, and shelf life of peanut butter.
4.1 Selecting the Best Peanut Variety
Spanish and Virginia peanuts are the most common varieties used for peanut butter production due to their rich oil content and taste. Choose high-grade peanuts with minimal moisture and no aflatoxin contamination.
4.2 Supplier Selection Tips
- Work with local farmers or cooperatives for consistent supply.
- Buy in bulk to lower per-unit cost.
- Inspect for mold or foreign materials before roasting.
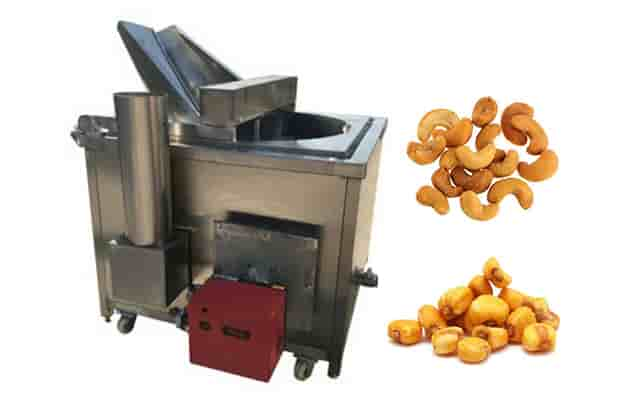

5. Üretim Süreci: Adım adım
The peanut butter production process is straightforward, but precision in each step ensures consistent quality and taste.
Adım 1: Temizlik
Taşları kaldır, toz, and foreign matter from the raw peanuts using sieves or air classifiers.
Adım 2: Kavurma
Roasting brings out the rich, nutty aroma. Ideal roasting temperature: 160–180 ° C (320–356°F) for about 30–40 minutes.
Adım 3: Soğutma
Kavurduktan sonra, peanuts must cool quickly to prevent overcooking.
Adım 4: Soyma
Use a dry peeling machine or manually remove skins. Skins can cause bitterness, so this step is crucial.
Adım 5: Bileme
Peanuts are ground into a paste using a colloid mill or peanut butter grinder. The number of grinding cycles affects the smoothness.
Adım 6: Karıştırma ve Homojenleştirme
Add ingredients like salt, şeker, or honey (isteğe bağlı). Homogenize for even consistency.
Adım 7: Dolum ve Paketleme
The final product is filled into jars, mühürlü, labeled, and ready for distribution.
6. Ambalaj ve etiketleme
Good packaging helps your product stand out and extends its shelf life.
6.1 Types of Packaging
- Plastic Jars – Affordable and lightweight.
- Glass Jars – Premium appearance, ideal for organic brands.
- Pouches – Economical and easy to store.
6.2 Labeling Requirements
Include:
- Brand name and logo
- Ingredients and nutritional facts
- Manufacturing date and batch number
- Expiry date
- Net weight
- Country of origin
Hatırlamak, visually appealing labels can strongly influence purchase decisions.
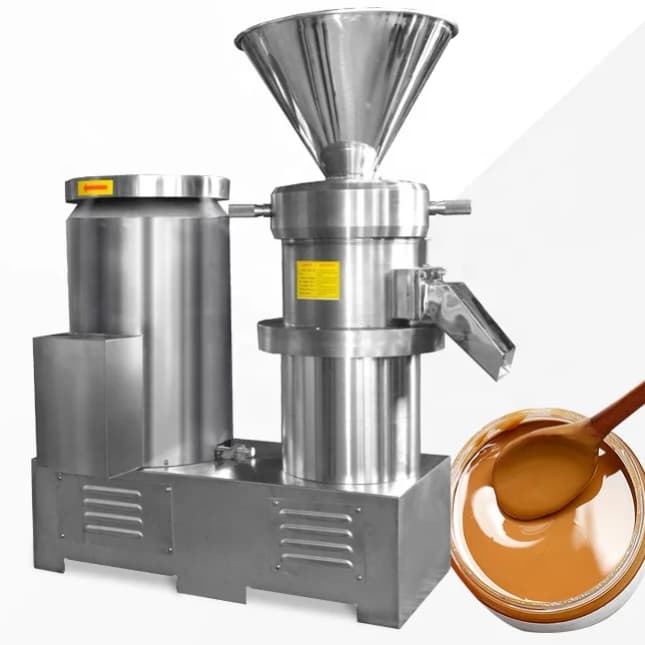

7. Ensuring Product Quality
Even small-scale producers must follow food safety regulations. Quality assurance builds trust and helps secure retail contracts.
7.1 Quality Control Steps
- Regular moisture testing
- Metal detection after grinding
- Sanitary production environment
- Use of food-grade stainless steel equipment
7.2 Certifications to Consider
Obtaining local certifications such as HACCP or ISO 22000 can boost your credibility and expand your market reach.
8. Marketing and Sales Strategies
Starting production is one thing—selling effectively is another. To maximize visibility and sales, small businesses must be creative and strategic.
8.1 Local Distribution
Approach local grocery stores, organic shops, and cafés. Offer samples or promotional discounts.
8.2 Çevrimiçi Pazarlama
Set up an e-commerce store or sell through platforms like Amazon, Lazada, or Shopee. Promote through:
- Social media ads
- Influencer collaborations
- Video marketing showing your production process
8.3 Markalaşma İpuçları
- Highlight “Made Locally” and “Natural Ingredients.”
- Use eco-friendly packaging.
- Share the story behind your brand.
9. How to Minimize Costs Without Cutting Quality
Low-budget production doesn’t mean compromising standards. Smart strategies can help you stay profitable even with small investments.
9.1 Start Small and Scale Gradually
Begin with one or two flavors—like classic smooth and crunchy—and expand once sales grow.
9.2 Optimize Raw Material Usage
Purchase peanuts during harvest seasons when prices are lowest.
9.3 Use Energy-Efficient Machines
Modern peanut butter machines, like those from DT Gıda Makinesi, are designed for low power consumption and high output efficiency, reducing operational costs significantly.
9.4 Rent or Lease Equipment
If purchasing new machines is too expensive initially, consider leasing. This reduces upfront costs while allowing full-scale operation.
10. Profitability and Return on Investment
10.1 Production Example
Let’s assume:
- Raw peanut cost: $1.5/kilogram
- Packaging and additives: $0.5/kilogram
- Total cost per kg = $2
- Selling price = $4–$5/kg
Profit per kilogram = around $2–$3, giving a gross margin of 50–60%.
At small-scale production of 500 kg/month, profit could reach $1,000–$1,500/month, growing with volume.
10.2 Scaling Up
As your brand builds recognition, reinvest profits to upgrade machinery and expand production. With high-quality machines and good marketing, a small unit can grow into a medium-sized peanut butter brand within 2–3 years.
11. Kaçınılması Gereken Yaygın Hatalar
- Skipping Market Research – Always understand your competition and target audience first.
- Using Poor-Quality Peanuts – This reduces flavor and shelf life.
- Ignoring Hygiene Standards – Leads to contamination and product recalls.
- Overinvesting Early – Start small, test demand, and scale gradually.
- Weak Branding – Even great products fail without strong packaging and marketing.

12. DT Gıda Makinesi
Starting peanut butter production on a low budget is not only possible—it can be highly profitable when planned correctly. With the right market approach, efficient machinery, and smart budgeting, even small entrepreneurs can compete successfully in this growing market.
DT Gıda Makinesi provides cost-effective solutions and reliable peanut butter making equipment that fit perfectly for startups and small-scale producers. By investing in quality machines, using high-grade peanuts, and implementing strong marketing, you can build a successful peanut butter business from scratch and expand as profits grow.
✅ Key Takeaways
- Küçük başlayın, focus on local demand first.
- Invest in efficient, energy-saving peanut butter machinery.
- Maintain strict hygiene and consistent quality.
- Build a strong brand identity.
- Scale gradually as your sales increase.
With passion, tutarlılık, and smart investment, your peanut butter business can grow into a sustainable and profitable enterprise—one jar at a time.
